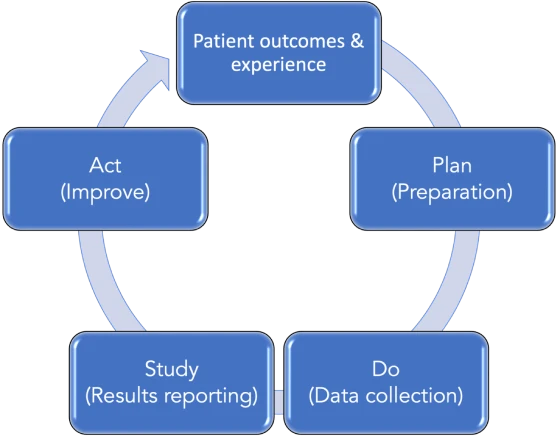
Projects
Before starting any project, answer these three questions:
- Objective: Define what you’re trying to achieve. Make objectives specific and quantifiable, like improving a PROM score by 10 points, rather than generic, unquantifiable goals, such as “achieve better patient wellbeing”.
- Measurement: Determine how you’ll measure improvement. Use our precise, pre-defined metrics to track progress. Quantitative data is more reliable than qualitative impressions.
- Changes for Improvement: Identify what changes you will need to make to achieve your desired objective.
SMART Criteria: Use SMART objectives – Specific, Measurable, Assignable, Relevant, and Time-bounded.
- Specific: Identify a clear area for improvement with precise objectives.
- Measurable: Set objectives that can be quantitatively measured.
- Assignable: Assign each objective to a person or team responsible for it.
- Realistic: Set challenging yet achievable objectives, considering available tools and uncontrollable factors.
- Time-bound: Define a clear timeline for achieving each objective.